Fit the Cauchy process on a phylogeny, using numerical optimization.
fitCauchy(
phy,
trait,
model = c("cauchy", "lambda"),
method = c("reml", "random.root", "fixed.root"),
starting.value = list(x0 = NULL, disp = NULL, lambda = NULL),
lower.bound = list(disp = 0, lambda = 0),
upper.bound = list(disp = Inf, lambda = NULL),
root.edge = 100,
hessian = FALSE,
optim = c("local", "global"),
method.init.disp = c("Qn", "Sn", "MAD", "IQR")
)Arguments
- phy
a phylogenetic tree of class
phylo.- trait
named vector of traits at the tips.
- model
a model for the trait evolution. One of
"cauchy"or"lambda"(see Details).- method
the method used to fit the process. One of
reml(the default),fixed.rootorrandom.root. See Details.- starting.value
starting value for the parameters of the Cauchy. This should be a named list, with
x0anddispthe root starting value and the dispersion parameter. The default initial values are computed from standard statistics used on (independent) Cauchy variables, see Details.- lower.bound
named list with lower bound values for the parameters. See Details for the default values.
- upper.bound
named list with upper bound values for the parameters. See Details for the default values.
- root.edge
multiplicative factor for the root dispersion, equal to the length of the root edge. Ignored if
method!=random.root.- hessian
if
TRUE, then the numerical hessian is computed, for confidence interval computations. Seecompute_vcov.- optim
if "local", only a local optimization around the initial parameter values is performed (the default). If "global", a global maximization is attempted using the "MLSL" approach (see
nloptr).- method.init.disp
the initialization method for the dispersion. One of "Qn", "Sn", "MAD", "IQR". Default to the "Qn" statistics. See Details.
Value
An object of S3 class cauphyfit, with fields:
x0the fitted starting value (for
method="fixed.root")- disp
the ml or reml estimate of the dispersion parameter
- lambda
the ml or reml estimate of the lambda parameter (for
model="lambda")- logLik
the maximum of the log (restricted) likelihood
- p
the number of parameters of the model
- aic
the AIC value of the model
- trait
the named vector of traits at the tips used in the fit
- y
the named vector of traits at the tips used in the fit
- n
the number of tips in the tree
- d
the number of dependent variables
- call
the original call of the function
- model
the phylogenetic model (one of
"cauchy"or"lambda")- phy
the phylogenetic tree
- method
the method used (one of
"reml","fixed.root","random.root")- random.root
TRUEifmethod="random.root"- reml
TRUEifmethod="reml"- root_tip_reml
name of the tip used to reroot the tree (for
method="reml")
Details
For the default model="cauchy", the parameters of the Cauchy Process (CP)
are disp, the dispersion of the process,
and x0, the starting value of the process at the root (for method="fixed.root").
The model assumes that each increment of the trait \(X\) on a branch going from node \(k\) to \(l\) follows a Cauchy distribution, with a dispersion proportional to the length \(t_l\) of the branch: $$X_l - X_k \sim \mathcal{C}(0, \mbox{disp} \times t_l).$$
Unless specified by the user, the initial values for the parameters are taken according to the following heuristics:
x0:is the trimmed mean of the trait, keeping only 24% of the observations, as advocated in Rothenberg et al. 1964 (for
method="fixed.root");disp:is initialized from the trait centered and normalized by tip heights, with one of the following statistics, taken from Rousseeuw & Croux 1993:
Unless specified by the user, x0 is taken to be unbounded,
disp positive unbounded.
The method argument specifies the method used for the fit:
method="reml":the dispersion parameter is fitted using the REML criterion, obtained by re-rooting the tree to one of the tips. See
logDensityTipsCauchyfor the default choice of the re-rooting tip;method="random.root":the root value is assumed to be a random Cauchy variable, centered at
x0=0, and with a dispersiondisp_root = disp * root.edge;method="fixed.root":the model is fitted conditionally on the root value
x0, i.e. with a model where the root value is fixed and inferred from the data.
In the first two cases, the optimization is done on the dispersion only, while in the last case the optimization is on the root value and the dispersion.
The function uses nloptr for the numerical optimization of the
(restricted) likelihood, computed with function logDensityTipsCauchy.
It uses algorithms BOBYQA
and MLSL_LDS
for local and global optimization.
If model="lambda", the CP is fit on a tree with branch lengths re-scaled
using the Pagel's lambda transform (see transf.branch.lengths),
and the lambda value is estimated using numerical optimization.
The default initial value for the lambda parameter is computed using adequate robust moments.
The default maximum value is computed using phytools:::maxLambda,
and is the ratio between the maximum height of a tip node over the maximum height of an internal node.
This can be larger than 1.
The default minimum value is 0.
References
Bastide, P. and Didier, G. 2023. The Cauchy Process on Phylogenies: a Tractable Model for Pulsed Evolution. Systematic Biology. doi:10.1093/sysbio/syad053.
Rothenberg T. J., Fisher F. M., Tilanus C. B. 1964. A Note on Estimation from a Cauchy Sample. Journal of the American Statistical Association. 59:460–463.
Rousseeuw P.J., Croux C. 1993. Alternatives to the Median Absolute Deviation. Journal of the American Statistical Association. 88:1273–1283.
See also
Examples
# Simulate tree and data
set.seed(1289)
phy <- ape::rphylo(20, 0.1, 0)
dat <- rTraitCauchy(n = 1, phy = phy, model = "cauchy",
parameters = list(root.value = 10, disp = 0.1))
# Fit the data
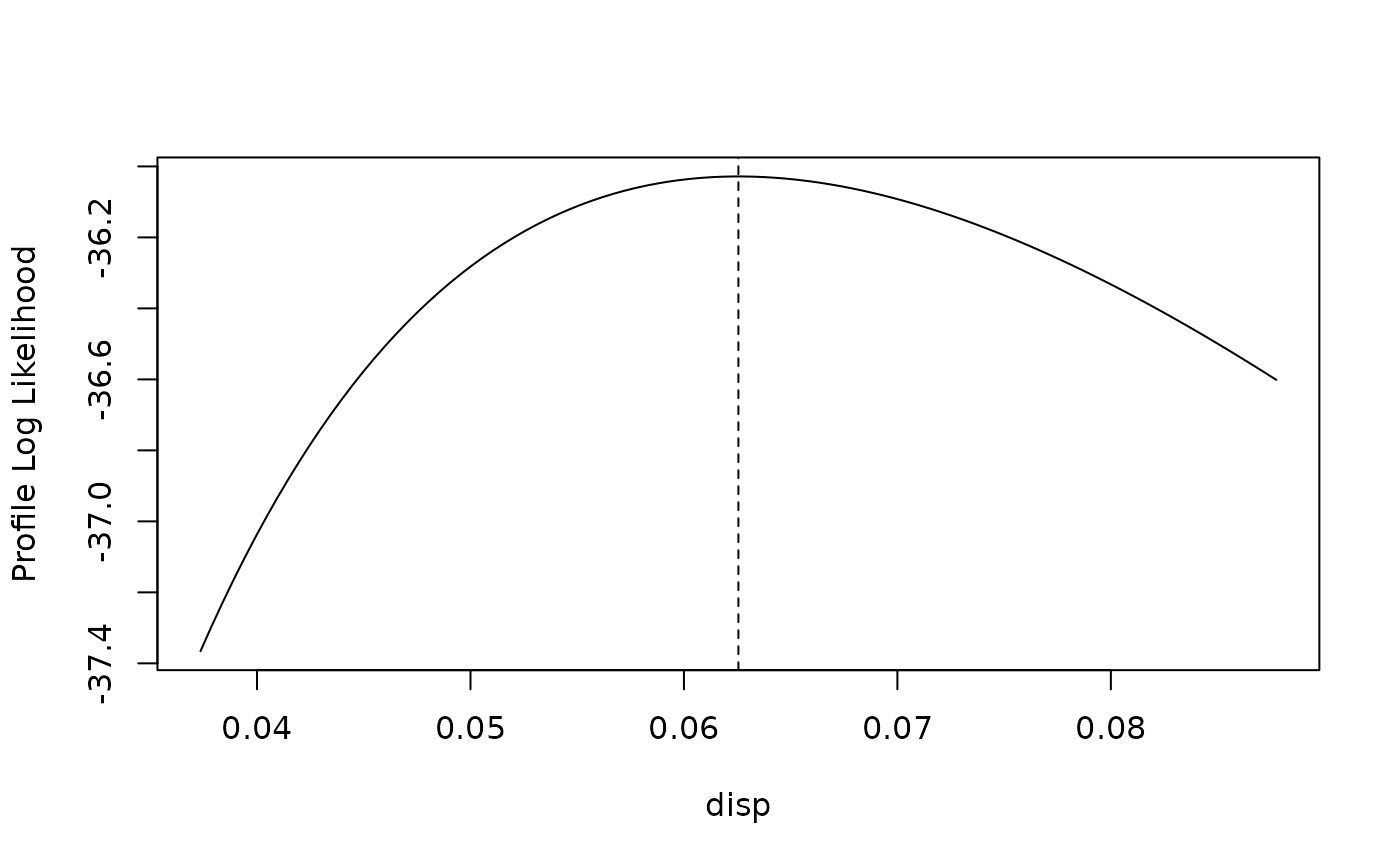
fit <- fitCauchy(phy, dat, model = "cauchy", method = "reml")
fit
#> Call:
#> fitCauchy(phy = phy, trait = dat, model = "cauchy", method = "reml")
#>
#> AIC logLik (restricted)
#> 74.06 -36.03
#>
#> Parameter estimate(s) using REML:
#> dispersion: 0.06255127
# Approximate confidence intervals
confint(fit)
#> Approximated asymptotic confidence interval using the Hessian.
#> 2.5 % 97.5 %
#> disp 0.0240104 0.1010921
# Profile likelihood
pl <- profile(fit)
plot(pl)